- Home
- portfolio
- APPLICATION
- Advancing Surgical Innovation with Medical-Grade Alloy Powders
Advancing Surgical Innovation with Medical-Grade Alloy Powders
Advancing Surgical Innovation with Medical-Grade Alloy Powders
3D-printed alloys revolutionize healthcare by enabling patient-specific implants, surgical tools, and biocompatible devices with unprecedented precision. Key alloys include titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) for bone integration, cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr) for wear resistance, and bioresorbable magnesium/zinc alloys for temporary implants. Applications span:
- Custom orthopedic implants (hip/knee replacements, spinal cages) with porous structures promoting bone growth;
- Patient-matched cranial/maxillofacial plates;
- Surgical guides optimizing complex procedures;
- Antimicrobial implants with surface-modified alloys (e.g., silver-coated titanium) fighting infections. Benefits include accelerated recovery, reduced surgery time (up to 50%), and elimination of traditional manufacturing constraints—ushering in an era of personalized, cost-effective medical solutions.
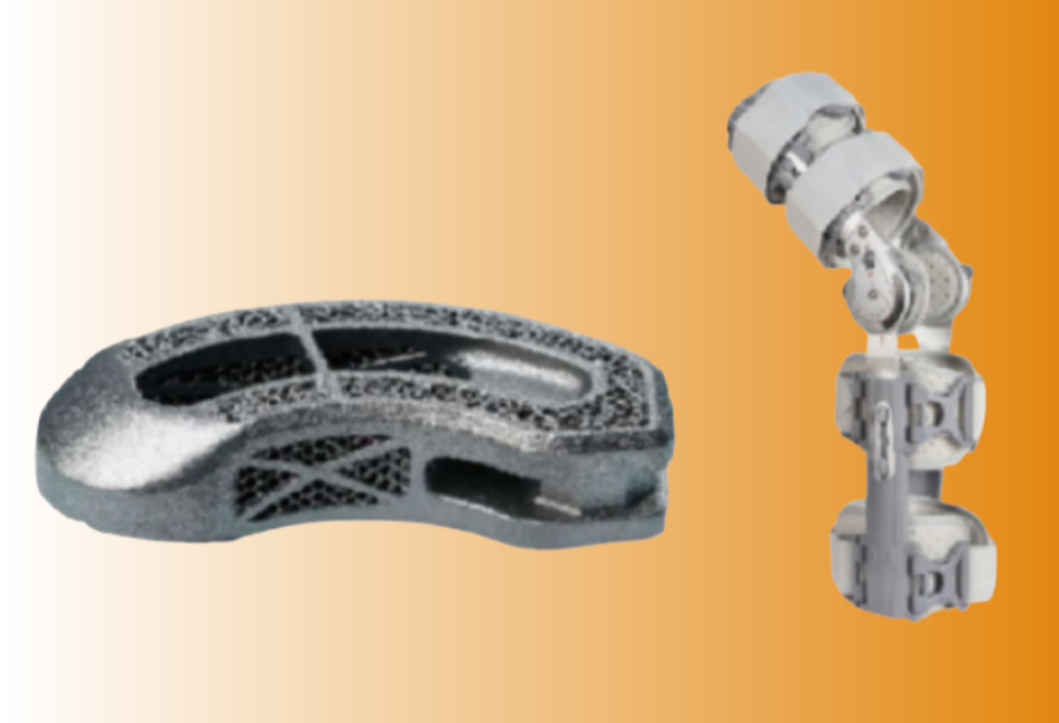

What revolutions do alloy powders bring to medical?
Alloy powders have sparked a medical revolution, empowering the development of innovative devices and treatments that were previously unimaginable. With the advent of additive manufacturing (AM), these powders have become the backbone of cutting-edge medical solutions, offering unprecedented precision, customization, and patient outcomes.
- Patient-Specific Implants
- Tissue Engineering Scaffolds
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Training Models and Simulators
- Surgical Guides and Templates
- Customized Prosthetics and Orthotics
Frontier material’s advanced alloy powders offer a transformative combination of properties that significantly elevate their performance in critical medical applications. Engineered with exceptional biocompatibility, these powders seamlessly integrate with human tissues, minimizing adverse immune responses and ensuring the long-term stability and safety of implants. Beyond biological harmonmaterialy, they deliver outstanding mechanical strength and superior corrosion resistance, enabling implants to reliably withstand the demanding physiological stresses and corrosive bodily environments over extended periods. Their precisely controlled particle morphology and composition grant excellent processability, particularly for additive manufacturing techniques, facilitating the creation of complex, patient-specific geometries with high accuracy and dimensional fidelity.