Exploring Metal Centrifugal Atomization Technology: From Principles to Applications
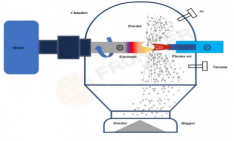
In modern industry and high-tech fields, the preparation of metal powders is of vital importance as it serves as the foundation for numerous advanced materials and products. Metal centrifugal atomization technology, as an efficient and high-quality method for preparing metal powders, is playing an increasingly significant role. Let’s now unveil the mystery of metal centrifugal atomization technology together.
The basic principle of metal centrifugal atomization
The core principle of metal centrifugal atomization is not complicated. Simply put, it utilizes the centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation to break liquid metal into fine droplets. These droplets rapidly cool and solidify during flight, ultimately forming metal powder.
Common methods of metal centrifugal atomization
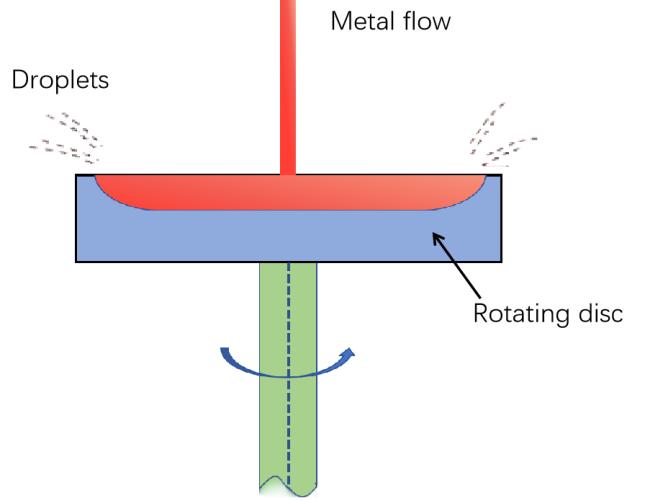
Rotary disk centrifugal atomization is a relatively common centrifugal atomization process. In this process, the high-speed rotating disk is the key component. When the liquid metal is sent to the center of the rotating disk, due to the high-speed rotation of the disk, the liquid metal will flow towards the edge of the disk under the action of centrifugal force. As the metal liquid reaches the edge of the disk, it will be rapidly flung out, forming fine droplets.
The rotational speed of the rotary disk, its diameter, and the flow rate of the liquid metal, among other factors, all affect the final particle size and shape of the metal powder. Generally speaking, the higher the rotational speed of the rotary disk, the smaller the particle size of the produced metal powder; and the larger the diameter of the disk, the longer the liquid metal stays on the disk, which also helps to form finer powder. The metal powder produced by this process has a relatively narrow particle size distribution and a more regular shape, and is often used in the manufacture of high-performance metal materials.
Rotary electrode centrifugal atomization features a unique working mode. It uses the metal to be atomized as the electrode. While the electrode rotates at high speed, the end of the electrode is heated and melted through methods such as electric arc or plasma. The molten metal is then thrown out from the end of the rotating electrode under the action of centrifugal force, forming droplets that cool and solidify into powder.
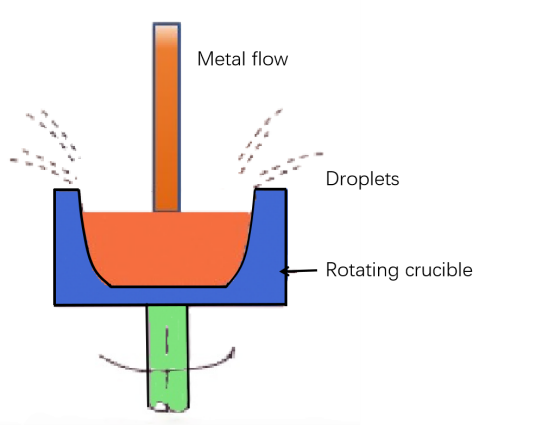
Rotating crucible centrifugal atomization is a process where liquid metal is placed in a rotating crucible. When the crucible rotates at high speed, the liquid metal is thrown out through small holes or gaps in the crucible wall, forming droplets and atomizing into powder. This process can handle large amounts of liquid metal and has a high production efficiency. The size, shape, and distribution of the small holes in the crucible wall directly affect the ejection speed and dispersion of the liquid metal, thereby influencing the particle size and quality of the powder. Rotating crucible centrifugal atomization is widely used in industrial production to manufacture various metal and alloy powders, meeting the demands of different industries for metal powders.

Summary
Metal centrifugal atomization technology offers us an effective method for preparing high-quality metal powders. Its principle is based on the centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation. Through different equipment and processes, metal powders with uniform particle size, high sphericity and high purity can be prepared.With the continuous advancement of science and technology, metal centrifugal atomization technology will also continue to innovate and improve, bringing us more surprises and application prospects.