Exploring Titanium Alloys and Their Additive Manufacturing Technology
In the world of metallic materials, titanium alloys stand out like a shining star, attracting the attention of numerous researchers and engineers with their outstanding properties and broad application prospects. Meanwhile, the rise of additive manufacturing technology has brought new opportunities for the processing and application of titanium alloys.
Titanium Alloys: The Versatile “All-Rounder”
Titanium alloys are alloys based on titanium with the addition of other alloying elements. They possess a series of remarkable characteristics. Firstly, they offer a perfect combination of low density and high strength. The density of titanium alloys is typically around 4.5 g/cm³, approximately 60% that of steel, yet their strength is comparable to that of high-strength steel. This makes them highly effective in the aerospace industry, where they are used to manufacture critical components such as aircraft fuselages, wings, and engine blades. By reducing the weight of aircraft, they help lower fuel consumption while ensuring the strength and reliability of the structure. Secondly, titanium alloys have excellent corrosion resistance. They can maintain good chemical stability in harsh environments such as seawater and chlor-alkali solutions and are not easily corroded. Therefore, in marine engineering fields, such as ship propellers and seawater desalination equipment, titanium alloys have been widely applied. Additionally, titanium alloys have good biocompatibility and do not cause immune responses in the human body, making them ideal materials for manufacturing artificial joints, dental implants, and other medical devices.
Additive Manufacturing: A Revolutionary Technology for Titanium Alloy Processing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is a technology that builds three-dimensional objects by layering materials. Compared with traditional subtractive manufacturing (such as cutting) and isomorphic manufacturing (such as casting and forging), additive manufacturing has significant advantages.
For titanium alloys, additive manufacturing technology can achieve precise manufacturing of complex structures. Traditional processing methods often face difficulties in manufacturing titanium alloy parts with complex internal structures or fine shapes, and the costs are high. However, additive manufacturing can directly build the required shapes by layering titanium alloy powders or wires based on computer design models, without the need for complex molds and tooling, significantly reducing the product development cycle and manufacturing costs.
Additive manufacturing can also achieve high-performance customization of materials. During the additive manufacturing process, the microstructure of titanium alloys can be precisely controlled by adjusting process parameters such as laser power and scanning speed, thereby obtaining different mechanical and physical properties. This enables titanium alloy parts to better meet the requirements of different application scenarios.

Application Prospects and Challenges
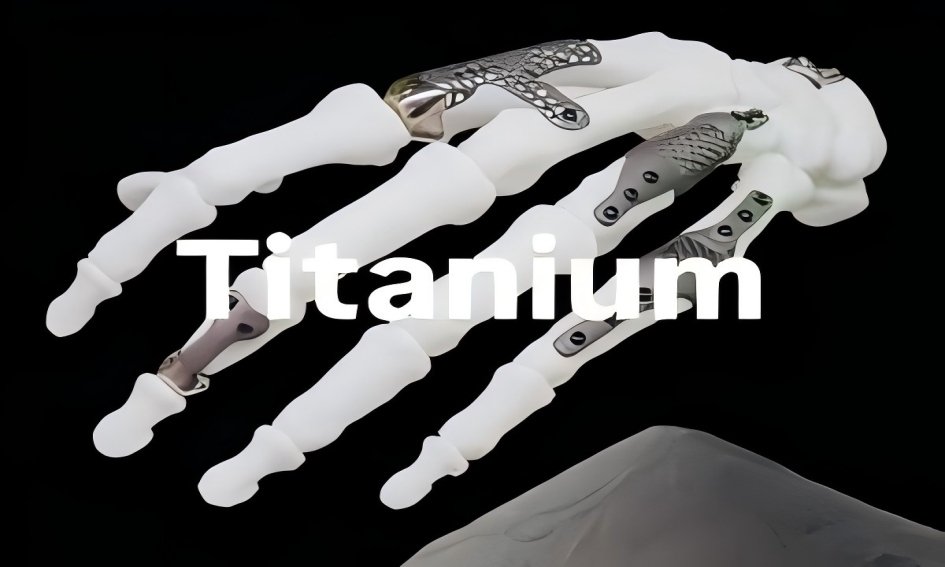
At present, titanium alloy additive manufacturing technology has been applied in fields such as aerospace, medical care, and automobiles to a certain extent. For instance, in the aerospace sector, additively manufactured titanium alloy parts have been successfully utilized in numerous advanced aircraft and spacecraft; in the medical field, customized titanium alloy implants have brought better treatment outcomes to patients.
However, titanium alloy additive manufacturing technology also faces several challenges. On the one hand, thermal stress and residual stress during the additive manufacturing process can easily cause part deformation and cracking, affecting the quality and performance of the parts. On the other hand, the surface quality and internal defect control of additively manufactured titanium alloy parts still need to be further improved. Additionally, the high cost of additive manufacturing equipment and relatively low production efficiency also restrict the large-scale application of this technology.
With the continuous advancement of technology, it is believed that titanium alloy additive manufacturing technology will be continuously improved and developed. In the future, it is expected to play a more significant role in more fields and make greater contributions to promoting the transformation and upgrading of the manufacturing industry and achieving high-quality development.