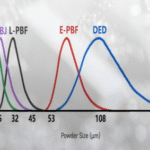
The Mystery of “Purity” in Metal Powders: The Significance of Oxygen, Nitrogen Content and Impurities

Did you know? Many common items in our lives, such as bicycle parts, electronic products, and even aerospace equipment, are made from metal powders! These seemingly ordinary powders actually hold many fascinating scientific secrets. Today, let’s explore the stories of oxygen, nitrogen, and impurities in metal powders and see how they act like “seasonings” to influence the properties of metals.
I. Oxygen: Friend and FoeOxygen makes up 21% of the air we breathe, but it is a “two-faced” element when it comes to metal powders. When exposed to air, the surface of metal powders gradually oxidizes, much like a cut apple turning yellow.
Negative effects of oxygen: It forms an oxide film that hinders the bonding between powder particles, affecting sintering quality and leading to defects such as cracks and pores in the product. In severe cases, it can cause the entire part to fail. Some reactive metals, such as titanium and aluminum, lose their original properties due to oxidation.
Positive effects of oxygen: However, engineers have discovered that a controlled amount of oxygen can bring benefits. For instance, in titanium alloys, a small amount of oxygen can increase the material’s strength. In diamond tools, precisely controlled oxygen content can enhance the bonding between metal and diamond.
Methods to control oxygen: Conduct production and storage in a vacuum or nitrogen-filled environment; Monitor oxygen content in real time during production to ensure it does not exceed the limit; Use special packaging for metal powders that are prone to oxidation.
II. Nitrogen: The Invisible Master
Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in air (comprising 78%) and is usually quite quiet, but it plays a crucial role in the world of metal powders.
Nitrogen’s Amazing Effects:It can significantly improve the strength of certain metals. For example, adding nitrogen to stainless steel can reduce the amount of chromium used, lowering costs. It acts as a shielding gas, preventing oxidation during high-temperature processing of metal powders. Under certain conditions, nitrogen can form a reinforcing phase with metals, improving material properties.The Dangers of Excessive Nitrogen: But more nitrogen isn’t always better. Excessive nitrogen can make metals brittle, just as too much baking powder can make bread tough and less fluffy. Therefore, scientists need to precisely control nitrogen levels, typically using specialized oxygen and nitrogen analyzers.
III. Impurities: “Destroyers” to Be Wary of
In addition to oxygen and nitrogen, other impurity elements may be present in metal powders. These act like “destroyers” in a team, affecting overall performance.
Common impurity issues: Hydrogen: Causes hydrogen embrittlement, causing the metal to fracture suddenly under stress; Sulfur, phosphorus, and other elements: Reduce the metal’s toughness and corrosion resistance;
Non-metallic inclusions: Affect the material’s uniformity and strength; Purity standards vary depending on the intended use: General use: A purity of approximately 99% is sufficient;3D printing powder: Purity requirement ≥ 99.9%;
Aerospace materials: Certain key elements must be present at levels below 0.01 ppm (equivalent to finding 1 gram of impurity in 100,000 tons of material).
IV. Technological Means: The Secret to Precise Control
To control these “playful” elements, scientists have developed a variety of high-tech methods:
Detection Technologies: Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Hydrogen Analyzers: Accurately measure the content of these elements;
Electron Microscopy: Observe the microstructure and composition distribution of powders;
Spectroscopic Analysis: Rapidly determine the chemical composition of materials;
Production Processes: Vacuum Melting: Reduces gas intrusion;
Inert Gas Shielding: Uses high-purity argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation; Online Monitoring: Real-time control of oxygen levels in the production environment.
V. Amazing Applications of Metal Powder
Now that we understand these secrets, let’s take a look at how metal powder is changing the world: 3D printing: Metal powders (such as titanium powder) are deposited layer by layer to create complex aerospace parts or medical implants. Powder metallurgy: Metal powders are pressed into shape and then sintered to produce mechanical parts such as gears and bearings. Specialty materials: Metal powder binders, such as those used in diamond tools, require precisely controlled oxygen content to ensure strength.
Conclusion: The Science and Art of Purity
The purity of metal powders isn’t a simple numbers game; it’s a complex balance of multiple elements. Just like cooking requires just the right seasoning, metal materials require precisely controlled ratios of their ingredients. By understanding the effects of oxygen, nitrogen, and impurities, scientists can design materials with superior properties, driving technological advancements. The next time you see an exquisite metal product, consider the countless scientific insights into purity it likely holds.