Three Minutes to understand the Core of Three Advanced Metal Powder Technologies


In the field of metal 3D printing, the quality of metal powder plays a decisive role in printing outcomes. The production of high-quality metal powder relies on advanced powder manufacturing technologies. Leveraging its professional technical team, FM has systematically developed schematic diagrams for three major high-end metal powder production technologies, elucidating their core principles.
1. Plasma Rotating Electrode Process (PREP): Centrifugal Force Forging Extreme Purity
Core Mechanism: High-speed rotation. A metal rod serves as a consumable electrode, which is melted at its end face under argon protection by a plasma arc.
Powder Formation Principle: Centrifugal tearing. The intense centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the electrode flings the molten metal film from the electrode edge, forming fine droplets.
Key Advantages:
✔ High Purity: The electrode melts itself, eliminating crucible contamination and minimizing impurities.
✔ Excellent Sphericity: Molten droplets naturally spheroidize under surface tension, achieving a sphericity of >98% and outstanding flowability.
✔ Low Satellite/ Hollow Powder: Process characteristics ensure dense powder with minimal satellite or hollow particles.
✔ Ideal for: Titanium and titanium alloys, superalloys, and other highly active materials requiring extreme purity.
(Schematic Diagram Source: Technical Team of FM)
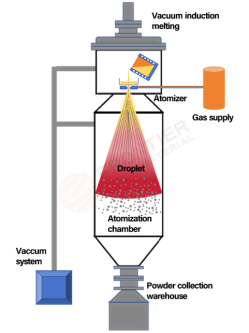
2. Vacuum Induction Melting Gas Atomization (VIGA): Precision Coordination of Melting and Atomization
Core Processes:
Vacuum Melting: Metal raw materials are melted in an induction furnace crucible under vacuum or inert gas protection, effectively degassing and reducing oxidation.
Guided Pouring: The molten metal flows steadily into the atomization zone through a guide tube.
Supersonic Atomization: High-pressure inert gas (typically argon or nitrogen) is expelled through a specialized nozzle, generating supersonic airflow that shatters the descending metal stream into fine droplets.
Key Advantages:
✔ Uniform Composition: Induction melting ensures high homogeneity of alloy components.
✔ High Yield of Fine Powders: Adjustable gas pressure and flow rate parameters enable precise control over powder particle size distribution, making it suitable for producing small to medium-sized powders.
✔ Wide Applicability: Capable of producing various alloys, including superalloys, specialty steels, aluminum alloys, and copper alloys.
Critical Technical Points: Guide tube design, melt superheat control, and nozzle optimization are essential for ensuring powder quality and consistency.
(Schematic Diagram Source: Technical Team of FM)
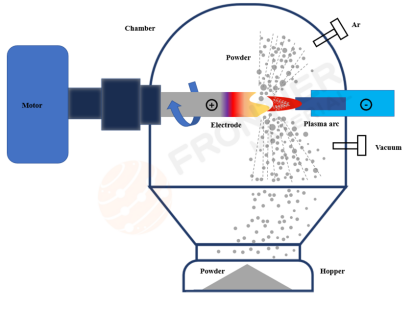
3. Electrode Induction Gas Atomization (EIGA): Contactless Melting for Ultimate Purity
Core Concept: Contactless melting, purer atomization.
Suspension Melting: A metal rod is vertically suspended and slowly fed into an induction coil, where the lower end is directly melted by the coil.
Droplet Formation & Atomization: Molten droplets detach from the rod tip under gravity or slight gas pressure and descend downward.
Gas Fragmentation: As the droplets fall, they are shattered into fine powder by converging high-pressure inert gas streams.
Key Advantages:
✔ Extreme Purity: The molten metal only contacts its solidified portion and inert gas, completely avoiding crucible contamination, with purity comparable to PREP.
✔ Specialized for Active Materials: Particularly suitable for highly active, oxidation-prone materials like titanium and zirconium alloys.
✔ Good Sphericity: Droplets achieve thorough spheroidization during atomization.
Technical Essence: Precise control of the balance between rod feed rate and melting speed, along with efficient energy transfer in gas atomization.
Conclusion: PREP, VIGA, and EIGA each offer distinct advantages, collectively achieving top-tier metal powders with high purity, excellent sphericity, and controllable particle size. FM has mastered the core principles and process intricacies of these technologies, continuously innovating to provide essential material foundations for advanced manufacturing fields such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) and metal injection molding (MIM).
(Schematic Diagram Source: Technical Team of FM)